Finally ready to test in EU: Google Bard
Potential ChatGPT killer?
Google has soft-launched their own AI chatbot Bard in the European Union. The chatbot, which was first released in the US in 2022, is designed to be a more natural and engaging way to interact with Google's products and services.
Bard is powered by Google's LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) AI technology, which allows it to understand and respond to natural language in a way that is indistinguishable from a human conversation. In addition to being able to speak its answers to you, Bard can also respond to visual prompts.
For example, if you ask Bard to "show me a picture of a cat," it will not only show you a picture of a cat, but it will also be able to tell you about the cat, such as its breed and where it is from.
The launch of Bard in the EU is a significant development, as it marks the first time that the chatbot has been made available outside of the US. Google says that it plans to continue to develop Bard and make it available in more regions in the future.
How is Bard different from other AI chatbots?
Bard is different from other AI chatbots in a number of ways. First, Bard is powered by Google's LaMDA AI technology, which gives it a much more natural and engaging conversational style. Second, Bard can respond to both spoken and visual prompts, which makes it more versatile than other chatbots that are only able to respond to text. Third, Bard is designed to be helpful and informative, and it will not engage in personal or emotional conversations.
What’s more?
In addition to the EU launch, Google is also adding a number of new features to Bard, including:
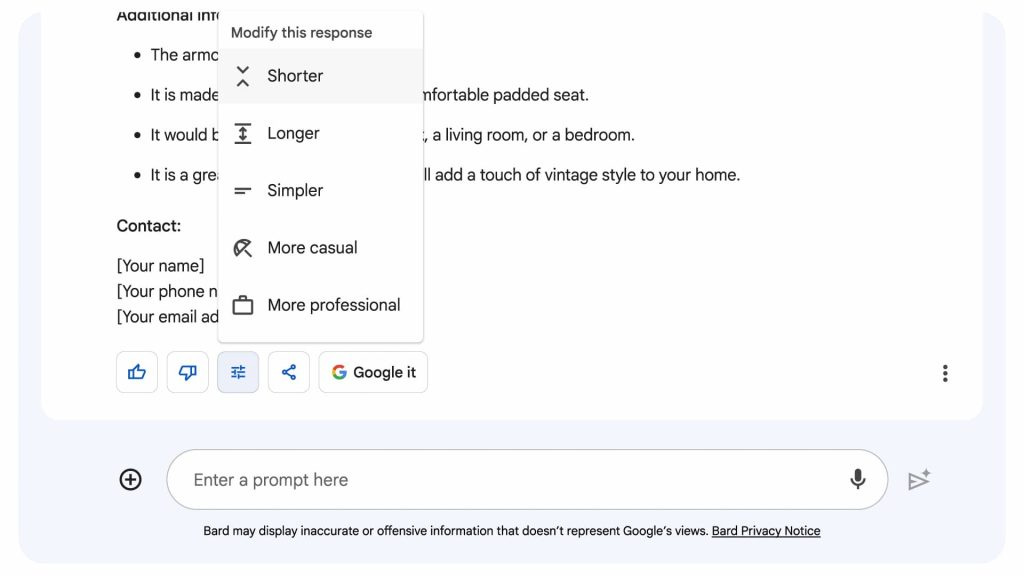
The ability to customize the tone and style of Bard responses. Users can now choose from five different options: Simple, long, short, professional, or casual.
The ability to have multiple conversations going at once. This is helpful for users who want to brainstorm ideas or research different topics simultaneously.
The ability to pin chats. This allows users to save an exchange (prompts + answers) in full as a quick way to return to past searches.
The ability to create links to Bard's responses. This makes it easy to share ideas and creations with others.
The ability to export Python code to Replit (Bas or me will share another substack article about Replit soon, hopefully). This allows users to take advantage of Replit's cloud-based development environment.
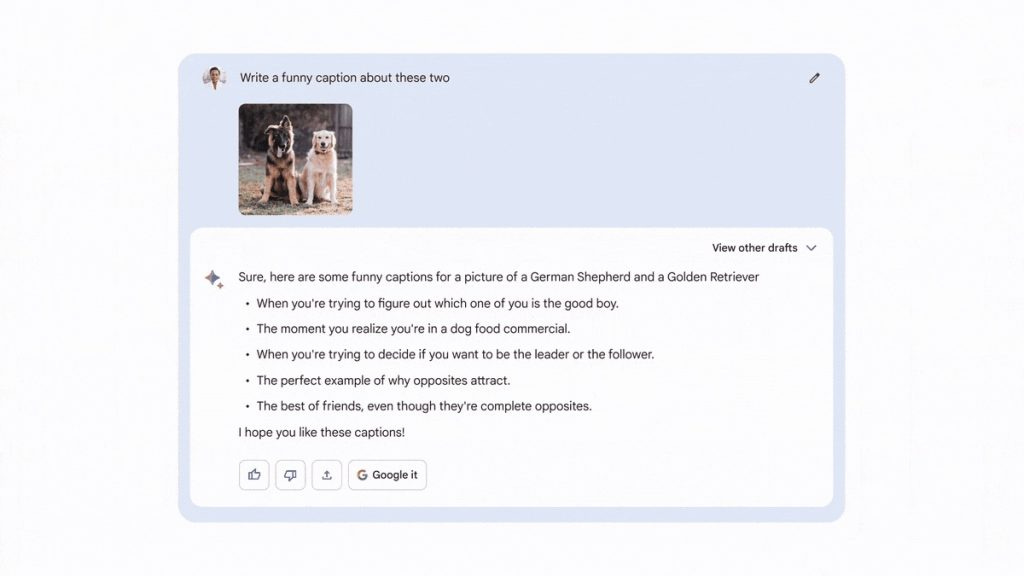
The ability to use Google Lens to ask questions about images. This is helpful for users who want to learn more about objects or scenes.
The future of Bard
Google says that it plans to continue to develop Bard and make it available in more regions in the future. The company also says that it is exploring ways to use Bard in new and innovative ways.
It will be interesting to see how Bard evolves in the years to come. With its natural language processing capabilities and its ability to respond to both spoken and visual prompts, Bard has the potential to become a powerful tool for communication and creativity.
Try it for yourself via: https://bard.google.com/